Omnichannel Retargeting Strategies: The Ultimate Guide
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive strategic analysis of omnichannel retargeting, a customer-centric approach that unifies marketing efforts across all channels to re-engage users with a seamless, personalized, and continuous brand narrative. In an era of fragmented customer journeys and increasing demand for personalization, moving beyond siloed, channel-specific retargeting is no longer an option but a strategic imperative for driving conversions, loyalty, and customer lifetime value.
The analysis reveals that successful omnichannel retargeting is contingent on three pillars: a unified data foundation powered by a Customer Data Platform (CDP), an intelligent orchestration engine driven by Artificial Intelligence (AI) and marketing automation, and a customer-obsessed organizational culture. While the benefits—including increased CLV, higher conversion rates, and enhanced brand loyalty—are substantial, implementation presents significant challenges related to technological integration, data privacy compliance, and organizational alignment.
Strategic recommendations point toward a phased transition from multichannel to omnichannel capabilities, beginning with the unification of customer data and the mapping of critical customer journeys. Businesses must prioritize the development of a robust first-party data strategy to mitigate the impact of third-party cookie deprecation. Investment in an integrated technology stack, particularly an actionable CDP, is critical for enabling the real-time personalization and cross-channel coordination that define true omnichannel engagement. Finally, performance measurement must evolve from channel-specific metrics to holistic, customer-centric KPIs like cross-channel conversion lift and CLV.
Redefining Engagement: From Channel-Centric to Customer-Obsessed
This section establishes the foundational concepts, clarifying the critical distinctions between prevailing marketing approaches and positioning omnichannel as the definitive evolutionary step.
The Evolution of Customer Engagement: A Critical Analysis of Multichannel, Cross-Channel, and Omnichannel Paradigms
The progression of digital marketing has given rise to several distinct paradigms for customer engagement: multichannel, cross-channel, and omnichannel. The distinction between these approaches is not merely semantic; it reflects a company’s core operating philosophy, organizational structure, and overall digital maturity. A company’s ability to execute a true omnichannel strategy serves as a direct proxy for its level of internal integration, data sophistication, and genuine commitment to customer experience over internal convenience.
Multichannel marketing is characterized by the use of multiple, but disconnected, channels that operate in isolation. The primary focus is on maximizing the performance of each individual channel, with teams often structured by platform (e.g., a social media team, an email team). This approach frequently leads to a fragmented and inconsistent customer experience, as the channels may deliver conflicting messages or even compete with each other for conversions.
Cross-channel marketing represents an advancement where channels are connected and complementary. This model allows customers to move between different platforms within a single journey, such as browsing a product online and picking it up in-store. Information is shared between these connected channels, creating a smoother and more integrated user experience than a purely multichannel approach.
Omnichannel marketing is the most advanced and holistic paradigm. It is a customer-centric strategy that integrates all available channels—both online and offline—into a single, seamless, and interactive ecosystem. The focus shifts entirely from the channel to the customer, creating a unified experience where the journey is fluid and the brand narrative is consistent, regardless of the touchpoint. This approach is fundamentally adaptive, evolving based on customer behavior rather than following predefined pathways, which necessitates advanced integration between all systems.
Defining Omnichannel Retargeting: A Unified Strategy for Re-engagement
Omnichannel retargeting is an advanced marketing strategy that re-engages potential customers across a unified ecosystem of multiple channels with personalized advertisements and messages based on their previous interactions with a brand. Unlike traditional, single-channel retargeting that operates within a silo, this strategy aims to create a seamless and consistent conversational narrative with the user, regardless of the device or platform they are using.
The core principle of this strategy is built on the premise that repeated, consistent, and contextually relevant exposure to a brand’s message across a customer’s preferred channels keeps the brand top-of-mind and significantly increases the likelihood of conversion. It moves beyond simply showing a user an ad for a product they viewed and instead orchestrates a series of interactions designed to guide them through the consideration process in a cohesive manner.
| Feature | Multichannel Retargeting | Omnichannel Retargeting |
|---|---|---|
| Core Philosophy | Channel-centric: Maximize reach and performance within each channel silo. | Customer-centric: Create a single, unified experience across all channels. |
| Customer Experience | Disconnected and often repetitive; a user sees the same ad on different platforms. | Seamless and continuous; the message evolves as the user moves between channels. |
| Data & Systems | Data is siloed by channel; systems are not integrated. | Data is centralized in a unified customer profile; systems are fully integrated. |
| Messaging Strategy | Static and channel-specific; the same offer is broadcast on multiple platforms. | Dynamic and adaptive; the next message is triggered by the customer’s last interaction. |
| Measurement of Success | Channel-specific metrics (e.g., Facebook ROAS, Email CTR). | Holistic, customer-centric KPIs (e.g., Customer Lifetime Value, cross-channel conversion lift). |
| Organizational Structure | Teams are often structured by channel, leading to internal competition. | Cross-functional teams collaborate to manage the end-to-end customer journey. |
Architecting the Omnichannel Foundation
This section details the strategic planning and foundational work required to build a successful omnichannel retargeting program. The transition from a channel-centric to a customer-centric model is fundamentally a data strategy challenge before it becomes a marketing strategy challenge. Without a unified data foundation, the subsequent steps of journey mapping, segmentation, and automation are rendered ineffective, highlighting the necessity of a top-down, cross-functional commitment to a centralized data architecture.
The Transition Playbook: A Step-by-Step Guide from Siloed Multichannel to Integrated Omnichannel Operations
Transitioning from a multichannel to an omnichannel framework is a structured process that requires careful planning and execution across data, strategy, and organizational culture.
- Step 1: Unify Data and Channels
The foundational step is to dismantle data silos by integrating all customer touchpoints—including website analytics, mobile app usage, CRM data, in-store POS systems, and social media interactions—into a centralized platform. This creates a single, 360-degree view of each customer, providing a comprehensive understanding of their behaviors and preferences across the entire ecosystem. Investing in technology that supports real-time data integration, such as a Customer Data Platform (CDP), is essential for this stage. - Step 2: Map the Customer Journey
With unified data, organizations can visualize the complete customer journey across all touchpoints. This process involves identifying where customers interact with the brand, what their experience is like at each stage, and how they move between channels. The resulting map serves as the strategic blueprint for identifying pain points, optimizing interactions, and ensuring consistent messaging throughout the buying process. - Step 3: Create Dynamic Customer Segments
The unified customer profile enables the creation of highly detailed and dynamic customer segments. These segments can be based on a rich combination of demographic data, purchase history, real-time behaviors (e.g., products viewed, content engaged with), and predictive analytics (e.g., likelihood to purchase). This level of segmentation is the key to powering hyper-personalized retargeting messages and offers. - Step 4: Automate Journeys for Scalability
To deliver timely, relevant experiences at scale, automation is critical. Marketing automation platforms, fueled by the unified data from a CDP, can be used to create “always-on” customer journeys. These automated workflows trigger personalized messages and offers based on specific customer actions, such as cart abandonment or repeat purchases, ensuring that the omnichannel strategy can operate 24/7 without requiring constant manual intervention. - Step 5: Secure Organizational Buy-In
An omnichannel strategy cannot succeed in a silo. It requires deep collaboration between marketing, sales, customer service, and IT departments. A critical, and often overlooked, step is to align internal incentives to reward holistic customer experience improvements rather than channel-specific performance.
Rewarding teams for maximizing sales in one channel without considering the impact on the overall customer journey can undermine the entire omnichannel effort.
Mapping the Unseen Journey: Advanced Techniques for Omnichannel Customer Journey Visualization
An omnichannel customer journey map is a strategic visualization of the entire process a customer undertakes to accomplish a goal, spanning all interaction channels and touchpoints. Unlike traditional linear models, it captures the complex, non-linear paths modern customers take, moving fluidly between online and offline environments. The purpose of this mapping is to transform the marketing objective from simply “driving a conversion” to “orchestrating a positive end-to-end experience,” where conversion becomes a natural outcome of resolving friction and enhancing engagement at every step.
The key components of a comprehensive journey map include:
- Customer Personas: Detailed profiles of target audience segments, including their goals, motivations, and communication preferences.
- Lifecycle Stages: The distinct phases of the journey, such as Awareness, Consideration, Purchase, and Loyalty.
- Touchpoints: Every point of interaction, from discovering a brand via a social media ad or a physical store to receiving post-purchase support through a chatbot.
- Customer Actions, Thoughts, and Feelings: Mapping what the customer is doing, thinking, and feeling at each stage to identify motivations and pain points.
- Opportunities: Identifying moments where a personalized interaction or a smoother channel transition could significantly improve the experience.
The mapping process itself is a strategic exercise involving several key steps:
- Define Personas and Goals: The process begins by selecting a specific customer persona and defining a clear objective for their journey (e.g., making a first purchase, joining a loyalty program).
- Identify All Touchpoints: All potential interaction points are cataloged, including digital channels (website, app, email, social media) and physical channels (in-store, events, call center).
- Visualize the Path: The customer’s path is outlined, documenting their actions, their likely emotional state (e.g., frustration at a broken link, delight at a personalized offer), and their channel-switching behaviors.
- Analyze and Optimize: The completed map is used to pinpoint friction points (e.g., inconsistent pricing between the app and the website) and identify opportunities for proactive engagement. This map is not a static document; it should be continuously updated and refined using real-time analytics and customer feedback.
The Tactical Execution Engine: Channels, Triggers, and Messaging
This section delves into the practical application of omnichannel retargeting, exploring the specific tools and techniques used to create compelling, cohesive campaigns that guide customers through their journey.
The Modern Channel Mix: Integrating Digital and Physical Touchpoints
A sophisticated omnichannel retargeting strategy leverages a diverse and integrated mix of channels to maintain a continuous conversation with the customer.
- Core Digital Channels: The foundation of the strategy lies in a coordinated mix of digital platforms. This includes email marketing for detailed follow-ups like cart abandonment reminders and nurture sequences; SMS and web push notifications for immediate, time-sensitive offers or in-store prompts; social media platforms for visually engaging dynamic product ads and story-based retargeting; programmatic display and video for brand reinforcement and delivering sequential ad narratives; and search engine marketing, particularly using retargeting lists for search ads (RLSA) to capture high-intent users who are already familiar with the brand.
- Bridging Online and Offline: A true omnichannel approach transcends the digital realm by incorporating physical touchpoints into the retargeting journey. This can manifest as in-store interactions where sales associates are equipped with tablets or POS systems that display a customer’s online browsing history and preferences, enabling personalized recommendations. It also includes leveraging location-based triggers, such as sending a push notification with a relevant offer when a customer is near a physical store, and coordinating digital messages with physical mailers or in-person events.
- Emerging Channels: Forward-thinking strategies are expanding to include emerging channels that are reshaping customer behavior. Connected TV (CTV) is becoming a powerful tool for upper-funnel retargeting, where an ad shown on a large screen can drive a “second-screen” search on a mobile device. Additionally, brands are preparing for the rise of voice assistants, considering how voice-based interactions can trigger or become part of a retargeting sequence.
Behavioral Intelligence: Leveraging High-Intent Triggers for Proactive Retargeting
Behavioral triggers are the engine of modern retargeting, enabling automated and timely responses to specific user actions (or inactions) that signal their intent and position in the customer journey. The effectiveness of these triggers is directly proportional to the speed and contextual relevance of the response. A simple, delayed, one-size-fits-all message is a hallmark of a multichannel system. In contrast, a true omnichannel system can react in real-time, adjusting the message and channel based on the customer’s most recent interaction, demonstrating a far more sophisticated level of intelligence.
Key high-value triggers include:
- Cart Abandonment: The most common and highest-intent trigger, targeting users who have added items to their shopping cart but failed to complete the purchase.
- Browse/Product View Abandonment: Re-engaging users who have shown interest by viewing specific products or categories but have not yet added anything to their cart.
- Time-Based Reactivation: Targeting dormant or lapsed customers who have not interacted with the brand for a defined period (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days) with “win-back” offers.
- High-Intent Engagement: Identifying users who exhibit deep engagement signals beyond simple page views, such as adding items to a wishlist, watching a product video to completion, or using an on-site calculator or configurator.
- Post-Purchase: Triggering automated campaigns after a purchase is completed to encourage a repeat purchase, request a review, or cross-sell complementary products and accessories.
Narrative-Driven Engagement: The Art and Science of Sequential Messaging
Sequential messaging transforms retargeting from a repetitive, direct-response tactic into a sophisticated brand-building and customer education tool. This technique involves presenting a series of ads or messages in a predetermined, logical order to the same user, effectively telling a cohesive story that guides them through the marketing funnel. This narrative approach is psychologically aligned with the decision-making process, reduces ad fatigue, and builds a stronger brand connection than simply showing the same “Buy Now” message repeatedly.
A typical sequence blurs the line between lower-funnel conversion tactics and mid-funnel content marketing, creating a more holistic journey:
- Beginning (Awareness/Reminder): The sequence often starts with a simple reminder, such as a display or social media ad showcasing the product the user previously viewed. The goal is to bring the brand back to the top of the user’s mind.
- Middle (Education/Consideration): This phase aims to address potential purchase barriers and build value. The user might be shown a video testimonial on a social platform, an article detailing the product’s benefits, or a third-party review. This educational content helps build trust and confidence.
- End (Conversion): The final stage is designed to drive action. The user may receive a targeted email or SMS with a compelling call-to-action, such as a limited-time discount, a free shipping offer, or a low-stock alert to create a sense of urgency.
The Technological Backbone: Powering Seamless Personalization at Scale
Executing a true omnichannel retargeting strategy is impossible without a sophisticated and deeply integrated technology stack. This infrastructure serves as the central nervous system, collecting data, making intelligent decisions, and activating personalized experiences across every customer touchpoint in real time.
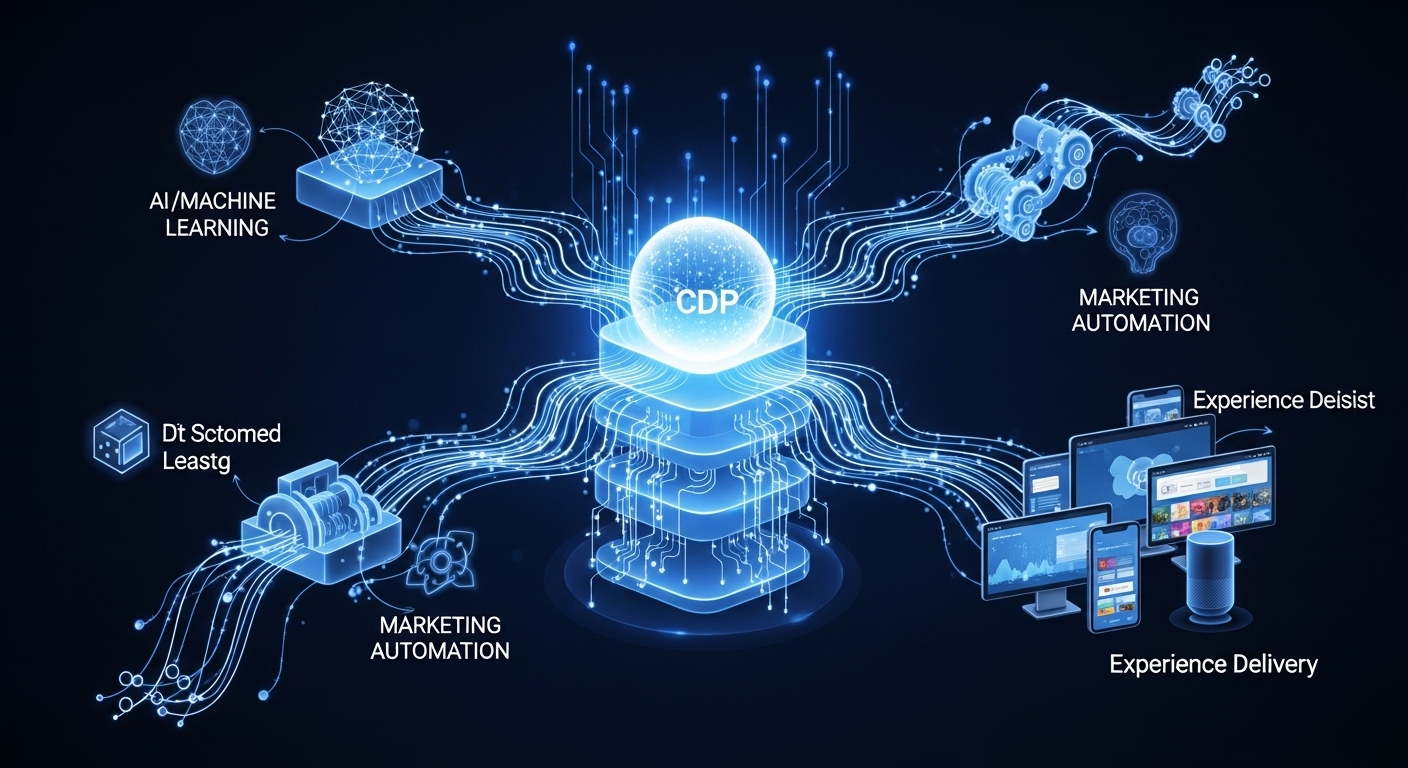
The Unified MarTech Stack: Core Components and Integration Architecture
An effective omnichannel stack is not merely a collection of tools but a fully integrated ecosystem where data flows seamlessly between layers. The core components can be understood within a layered architecture:
- Data Layer: This is the foundation, responsible for collecting and unifying customer data from all sources. The central component here is a Customer Data Platform (CDP).
- Decisioning Layer: This is the intelligence engine of the stack. It uses Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning to analyze the unified data for predictive analytics, advanced segmentation, and journey orchestration.
- Activation/Delivery Layer: This layer executes the campaigns based on the decisions made by the intelligence layer. It includes marketing automation platforms and channel-specific tools like Email Service Providers (ESPs), SMS gateways, and advertising platforms.
- Experience Layer: This layer is responsible for delivering the final content to the user.
It is powered by Content Management Systems (CMS), with headless CMS architectures being particularly effective for delivering consistent brand content across diverse endpoints like websites, mobile apps, and in-store kiosks.
Data Collection & Unification
- Component: Customer Data Platform (CDP)
- Core Function: Ingests data from all sources, performs identity resolution, and creates a unified customer profile.
- Example Vendors/Technologies: Insider, Salesforce CDP, Twilio Segment, Tealium.
Customer Profile & Identity
- Component: Identity Graph
- Core Function: Connects customer identifiers (cookies, device IDs, emails) across devices and platforms to a single persistent profile.
- Example Vendors/Technologies: LiveRamp, Neustar, The Trade Desk Unified ID 2.0.
Analytics & Decisioning
- Component: AI / Machine Learning Engine
- Core Function: Analyzes data for predictive scoring (e.g., likelihood to buy), segmentation, and determining the “next best action”.
- Example Vendors/Technologies: Salesforce Einstein, Adobe Sensei, Custom-built models.
Orchestration & Activation
- Component: Marketing Automation Platform
- Core Function: Executes automated, trigger-based workflows and cross-channel campaigns using data from the CDP.
- Example Vendors/Technologies: Customer.io, HubSpot, Braze, Iterable.
Experience Delivery
- Component: Headless Content Management System (CMS)
- Core Function: Manages content in a central repository and delivers it via API to any front-end channel (web, mobile, kiosk, etc.).
- Example Vendors/Technologies: Contentful, Contentstack, Shopify (Headless).
The Central Nervous System: A Deep Dive into Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) and Marketing Automation
The integration of a CDP with a marketing automation platform is the critical link that enables true omnichannel personalization. While these tools are sometimes confused, they serve distinct but complementary functions.
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is the system of record for customer data. Its primary functions are to ingest data from disparate sources (e.g., CRM, e-commerce platform, website analytics, offline POS), cleanse and standardize that data, and perform identity resolution to stitch together various identifiers into a single, persistent, and unified customer profile—the coveted “360-degree view”.
A Marketing Automation Platform, on the other hand, is a system of engagement. Its strength lies in executing workflows, such as sending an email sequence or a push notification based on a trigger. However, without a CDP, automation platforms often operate with fragmented, incomplete, or latent data, limiting their ability to orchestrate truly cross-channel journeys. The CDP enriches the automation engine by feeding it a clean, comprehensive, and real-time stream of customer data. In essence, the CDP provides the rich “who” and “what” (the unified profile and their behaviors), empowering the automation platform to execute the “how” and “when” (the right message on the right channel at the right time) with far greater precision.
A more advanced category, the Actionable CDP, combines these functions into a single platform. These systems not only unify data but also have built-in activation channels (e.g., email, SMS, on-site personalization) and journey orchestration capabilities, offering a more streamlined, all-in-one solution. The choice between a composable stack (using a standalone “Access CDP” to feed best-of-breed activation tools) and an integrated “Actionable CDP” is a key strategic decision, balancing flexibility against speed and simplicity.
The Intelligence Layer: The Role of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning form the decision-making brain of the modern omnichannel stack, transforming it from a system that executes pre-programmed rules to one that learns, predicts, and optimizes autonomously.
- Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms analyze the vast datasets within the CDP to predict future customer behavior. This includes calculating scores for each user, such as their likelihood to purchase, their predicted lifetime value, or their risk of churning. This allows marketers to proactively engage customers with the right message before they even take an explicit action, such as targeting a user with a high “likelihood to purchase” score with a special offer.
- AI-Powered Journey Orchestration: Moving beyond simple “if-then” triggers, AI-powered orchestration dynamically determines the “next best action” for each individual customer. By analyzing a user’s real-time behavior against their historical data and predictive scores, the system can decide whether the optimal next step is to send an email, show a social media ad, deliver a push notification, or even suppress messaging to avoid fatigue. This marks a significant evolution from manually mapping a static journey to allowing the system to autonomously optimize the path for each user to achieve a specific goal, such as maximizing CLV.
- Dynamic Personalization and Content: AI enables hyper-personalization at a scale that is impossible to achieve manually. It can dynamically tailor ad creatives, product recommendations, email content, and website layouts for each user in real time. For example, an e-commerce homepage can be instantly reconfigured to feature products related to a category the user just browsed in the mobile app, creating a truly seamless and contextually relevant experience.
Measuring What Matters: Attribution and Performance in a Complex Ecosystem
Measuring the effectiveness of an omnichannel retargeting strategy requires a fundamental shift away from siloed, channel-specific metrics toward holistic, customer-centric models. An over-reliance on traditional KPIs can lead to value-destructive optimization, where decisions that improve a single channel’s performance inadvertently harm the overall customer journey and business outcome. For instance, cutting the budget for a non-clickable Connected TV ad because of its zero click-through rate ignores its potential to significantly lift conversions on subsequent search ads, thereby undermining the entire strategy.
Beyond Last-Click: Implementing Multi-Touch Attribution Models
In a complex omnichannel journey, a customer may interact with multiple touchpoints before converting. A last-click attribution model, which assigns 100% of the credit to the final interaction, is fundamentally flawed as it ignores the crucial, value-building role of all preceding touchpoints. To gain an accurate understanding of performance, organizations must adopt more sophisticated multi-touch attribution models. The choice of model is not merely a technical decision but also a political one, as it directly impacts how budgets are allocated and how team performance is perceived across the organization.
Common models include:
- Linear: This model distributes credit equally across every touchpoint in the conversion path. It is simple to implement but may undervalue more influential interactions.
- Time-Decay: This model gives more credit to touchpoints that occur closer in time to the conversion. It recognizes that interactions just before a purchase are often more influential.
- Position-Based (U-Shaped): This model assigns a higher percentage of credit (e.g., 40% each) to the first and last interactions, with the remaining credit distributed among the middle touchpoints. It values both the initial discovery and the final conversion-driving touch.
- Data-Driven: This is the most advanced model. It uses machine learning algorithms to analyze all converting and non-converting paths to determine the actual incremental contribution of each touchpoint. While the most accurate, it is also the most complex to implement and requires a significant volume of data.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Holistic Success
The focus of measurement must shift from channel-level efficiency metrics (e.g., Email Open Rate, Ad CTR) to customer-centric KPIs that reflect overall business impact.
Primary Business Outcome KPIs:
- Customer Lifetime Value: The ultimate measure of success. A successful omnichannel strategy increases the total predicted revenue a customer will generate over their entire relationship with the brand by fostering loyalty and repeat purchases.
- Customer Retention Rate (CRR) / Churn Rate: A direct measure of customer loyalty. Seamless, personalized experiences reduce customer frustration and increase the likelihood that they will remain with the brand over time.
- Cross-Channel Conversion Rate / Lift: This metric compares the conversion rate of customers who are engaged across multiple channels versus those who interact with only a single channel.
A positive lift provides clear evidence of the synergistic effect of the omnichannel strategy.
Secondary Diagnostic KPIs:
- Average Order Value (AOV): Often increases as a result of more effective, data-driven cross-selling and upselling opportunities presented throughout the journey.
- Purchase Frequency: Engaged and loyal customers tend to make purchases more often.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) / Net Promoter Score (NPS): These survey-based metrics provide a direct pulse on the customer’s perception of the experience and their willingness to advocate for the brand.
| KPI Category | KPI Name | Definition | Strategic Importance for Omnichannel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Value & Loyalty | Customer Lifetime Value | The total predicted net profit attributed to the entire future relationship with a customer. | The ultimate metric; reflects the long-term success of building customer relationships over single transactions. |
| Customer Retention Rate (CRR) | The percentage of existing customers who remain customers over a specific period. | Directly measures loyalty and the effectiveness of the seamless experience in preventing customer churn. | |
| Conversion & Efficiency | Cross-Channel Conversion Rate | The conversion rate of users who have interacted with more than one channel. | Proves the synergistic value of channel integration; should be measured against single-channel conversion rates. |
| Average Order Value (AOV) | The average total of every order placed with a merchant over a defined period. | Indicates the effectiveness of personalized cross-selling and upselling within the customer journey. | |
| Customer Experience | Net Promoter Score (NPS) | A measure of customer loyalty based on their likelihood to recommend the brand. | Gauges overall satisfaction and brand advocacy, which are direct outcomes of a positive omnichannel experience. |
| Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) | A measure of how satisfied customers are with a specific interaction or the overall experience. | Provides granular feedback on specific touchpoints within the journey, helping to identify and fix friction points. |
Navigating the Headwinds: Privacy, Cookies, and Future-Proofing Strategy
This section addresses the most significant external challenges to retargeting and outlines the strategic pivots required to build a sustainable, future-proof approach. The evolving privacy landscape is not a roadblock to omnichannel marketing but rather an accelerator of its most critical components: a first-party data foundation and a commitment to building customer trust through transparent value exchange.
The Post-Cookie Reality: Impact of Data Privacy Regulations on Retargeting
The digital advertising ecosystem is undergoing a seismic shift driven by both regulatory and technological forces. The deprecation of third-party cookies by major browsers like Google Chrome, combined with stringent data privacy regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), is rendering traditional retargeting methods obsolete.
- Regulatory Impact: Laws like GDPR require businesses to obtain explicit, informed consent from users before collecting and processing their personal data for advertising purposes. They also grant consumers the right to access, rectify, and erase their data, effectively allowing them to opt out of retargeting pools. This significantly reduces the scale of addressable audiences for campaigns that rely on third-party data.
- Technological Impact: Browser-level privacy features, such as Apple’s App Tracking Transparency (ATT) framework and Google’s Privacy Sandbox initiative, fundamentally restrict the ability to track users across different websites and applications. This cross-site identification is the core mechanism that powers third-party cookie-based retargeting, and its demise makes this form of advertising impossible in its current state.
Strategic Pivot to First-Party and Zero-Party Data
In the post-cookie world, the most valuable asset for any organization is the data it collects directly from its customers with their consent. A future-proof retargeting strategy must be built on this foundation.
- First-Party Data Strategy: The primary strategic response is to prioritize the collection and activation of first-party data. This includes information gathered directly from customer interactions, such as email addresses and phone numbers provided during account creation, on-site browsing behavior, purchase history, and app usage data. This data is more accurate and reliable than third-party data and can be used for retargeting with proper consent.
- Zero-Party Data: An even more powerful form of data is zero-party data, which customers intentionally and proactively share with a brand. This can include preferences, purchase intentions, and personal context, often collected through interactive quizzes, surveys, preference centers, or conversational interfaces. This data is explicit and highly valuable for deep personalization.
- Building the Asset: To encourage customers to share this valuable data, businesses must create clear value exchanges. This involves offering tangible benefits in return for information, such as personalized recommendations, exclusive content, early access to products, or loyalty program rewards. The goal is to build a trusted relationship where customers are willing to provide data because they receive a better experience in return.
The Next Frontiers: Integrating Emerging Channels
As traditional retargeting methods wane, the importance of innovating with new channels and technologies grows.
- Connected TV (CTV): The rise of CTV is fundamentally changing the retargeting funnel by reintroducing a “broadcast” element that must be measured by influence rather than direct clicks. Omnichannel strategies can now create sequences that span the living room and personal devices. TV-to-Web retargeting involves showing a non-clickable ad on CTV and then following up with a targeted ad on the viewer’s mobile phone or laptop. Conversely, Web-to-TV retargeting can re-engage a website visitor with a high-impact ad on their television screen. Executing this requires sophisticated cross-device identity resolution, often done at the household level using IP addresses and other signals.
- Voice and Visual Search: As consumers increasingly use voice assistants and visual search for product discovery, brands must adapt. This involves optimizing product data and content for these new modalities and integrating them into the omnichannel journey. For example, a voice query for a product could trigger a retargeting ad on a user’s mobile app, or a visual search could add an item to a user’s profile for later retargeting.
- Post-Cookie Solutions: The industry is actively developing alternative identification and targeting methods. These include people-based advertising, which uses hashed email addresses or other persistent identifiers to target users across platforms; identity graphs, which connect various user identifiers to a single profile; and a renewed focus on contextual advertising, which targets users based on the content they are consuming rather than their personal data.
Case Studies in Omnichannel Excellence: A Deep-Dive Analysis
This section provides a detailed analysis of how leading brands across different industries have successfully implemented omnichannel strategies, translating theory into practice and demonstrating quantifiable results. These case studies highlight a common thread: the central role of a loyalty program or mobile application as the hub for data collection and customer interaction, which then fuels a seamless experience across both digital and physical realms.
The Loyalty Ecosystem: Starbucks
- Core Strategy: Starbucks’ omnichannel strategy is centered around its Starbucks Rewards program and mobile app, which are designed to seamlessly integrate the digital and physical coffee-buying experience. The app functions as a central hub for mobile ordering, digital payments, and the accumulation and redemption of loyalty points (“Stars”).
- Technology & Execution: The platform creates a unified customer profile that syncs order history, personalized preferences, and rewards status across all devices and physical stores. The company’s “Digital Flywheel” strategy employs a cloud-based AI engine that delivers personalized offers and recommendations based on a customer’s purchase history, time of day, and even local weather conditions. Starbucks has also formed strategic partnerships with technology leaders like Microsoft for generative AI development and Amazon for in-store experience innovation to continually enhance its capabilities.
- Results: The strategy has been remarkably successful at fostering loyalty and driving revenue. The Starbucks Rewards program now boasts over 34 million members and is responsible for driving nearly 60% of the company’s sales in the U.S. This ecosystem creates a deep emotional connection with customers, leading to high rates of repeat business and engagement.
The Experiential Retail Model: Sephora
- Core Strategy: Sephora has mastered the art of blurring the lines between online and offline retail. The strategy uses technology to enrich the in-store experience while simultaneously bringing the interactive, consultative nature of the physical store to its digital platforms. The Beauty Insider loyalty program serves as the primary engine for data collection, fueling personalization across the ecosystem.
- Technology & Execution: The Sephora mobile app is the “glue” that holds the experience together.
It features an AI-powered “Virtual Artist” tool that uses augmented reality (AR) to allow customers to virtually try on makeup. In physical stores, beauty advisors are equipped with iPads running a “clienteling app” that provides access to a customer’s unified profile, including online browsing history and past purchases, enabling highly personalized in-store consultations. Digital tools like “Color IQ” scan a customer’s skin to find the perfect foundation match, further integrating technology into the physical journey. To ensure a frictionless transaction process, Sephora partnered with J.P. Morgan Payments to create a centralized platform that seamlessly handles purchases, returns, and exchanges across all channels.
Results:
The impact of this strategy is evident in customer behavior and financial performance. Members of the Beauty Insider program spend 15 times more than non-members, and app users spend twice as much annually as the average customer. This integrated approach contributed to a 50% increase in sales to $6 billion in the two years leading up to 2019.
The Magic of Integration: Disney
Core Strategy:
Disney’s objective is to create a completely immersive and frictionless entertainment experience through its MyMagic+ platform. This system acts as a “Journey Bridge,” masterfully connecting the pre-visit planning phase, the in-park experience, and post-visit engagement into a single, continuous narrative.
Technology & Execution:
The core of the system is the combination of the “My Disney Experience” mobile app and the RFID-enabled “MagicBand.” Before the trip, guests use the app to plan itineraries and make reservations. During the visit, the MagicBand serves as an all-in-one device: a hotel room key, park ticket, payment method, and ride reservation pass. The platform collects vast amounts of real-time data on guest movements and preferences, which is used to optimize park operations (e.g., managing queue times) and create personalized “magical moments,” such as costumed characters greeting a child by name.
Results:
While specific ROI figures on the over $1 billion investment are proprietary, the strategic goals were to increase guest spending through convenience, improve operational efficiency by managing park flow, and, most importantly, enhance the uniquely “magical” experience that drives Disney’s unparalleled customer loyalty and high rate of repeat visits.
The Financial Services Transformation: Bank of America
Core Strategy:
Bank of America has implemented an omnichannel strategy focused on providing proactive, personalized, and seamless service across its digital and physical banking channels. The cornerstone of this strategy is its powerful digital banking platform, headlined by the AI-powered virtual financial assistant, “Erica”.
Technology & Execution:
Erica acts as a central point of interaction, handling hundreds of millions of client queries and providing proactive financial insights across the consumer mobile banking app, Merrill investment platforms, and the corporate CashPro platform. The digital ecosystem is further unified through integrated services like Zelle for peer-to-peer payments, mobile check deposit, and a robust system of real-time alerts for account activity, creating a cohesive and convenient user experience.
Results:
The adoption and impact of this digital-first omnichannel strategy are significant. In 2024, digital interactions surged to 26 billion, a 12% year-over-year increase. A record 55% of all bank sales were completed through digital channels. The Erica assistant has handled over 2.5 billion interactions since its launch, and Zelle transactions on the platform reached 1.6 billion, valued at $470 billion, demonstrating a massive shift in customer behavior toward integrated digital channels.
| Brand | Industry | Core Omnichannel Strategy | Key Enabling Technology | Reported Metrics / Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Starbucks | Food & Beverage | Loyalty program and mobile app integrating digital ordering/payment with the in-store experience. | Mobile App, “Digital Flywheel” AI Engine, Starbucks Rewards Platform. | Loyalty members drive nearly 60% of sales; 34 million members. |
| Sephora | Retail (Beauty) | Blurring online/offline with in-store tech and an app that brings the store experience online. | Mobile App with AR (“Virtual Artist”), In-Store iPads, Color IQ, Unified Commerce Platform. | Loyalty members spend 15x more; app users spend 2x more annually. |
| Disney | Entertainment | A fully integrated and frictionless guest experience from pre-planning to post-visit engagement. | MyMagic+ Platform, RFID “MagicBands,” My Disney Experience App. | $1B+ investment aimed at increasing guest spending, loyalty, and operational efficiency. |
| Bank of America | Financial Services | Proactive, personalized service through a unified digital banking platform. | “Erica” AI Virtual Assistant, Integrated Mobile Banking App, CashPro Platform. | 26 billion digital interactions (+12% YoY); 55% of sales via digital channels. |
| Walmart | Retail | Leveraging vast physical store network as fulfillment hubs for a robust e-commerce operation. | Mobile App (Store Maps, Scan & Go), Integrated Inventory System, Walmart Pay. | 22% increase in global e-commerce sales. |
| McDonald’s | Food & Beverage | Centralized loyalty program (MyMcDonald’s Rewards) that unifies mobile app, in-store, and delivery channels. | MyMcDonald’s Rewards Program, Mobile App, In-Restaurant Digital Kiosks. | Rewards program powers $30 billion in omnichannel sales. |
Strategic Recommendations and Concluding Analysis
This final section synthesizes the report’s findings into an actionable blueprint for business leaders and provides a forward-looking perspective on the evolution of customer re-engagement.
Actionable Blueprint for Implementation: A Phased Approach
The transition to a fully realized omnichannel retargeting strategy is a significant undertaking that should be approached in deliberate phases to manage complexity, demonstrate value, and build organizational momentum.
Phase 1: Foundation (Months 1-6)
This initial phase focuses on establishing the necessary groundwork. It begins with a comprehensive audit of all existing customer channels and data sources to understand the current state of fragmentation. The most critical objective is to secure executive-level buy-in for a cross-functional data unification project, framing it as a core business initiative rather than a marketing-only project. The key investment during this phase is in a Customer Data Platform (CDP), followed by the technical work of integrating primary data sources such as the CRM, e-commerce platform, and website analytics.
Phase 2: Activation (Months 7-12)
With a foundational data layer in place, the focus shifts to activation. This involves developing initial omnichannel customer journey maps for one or two high-value segments (e.g., new customers, high-spending loyalists). Based on these maps, pilot programs for key behavioral triggers, such as cart abandonment, should be launched across two or three tightly connected channels (e.g., email, social media ads, and web push notifications). Concurrently, the organization must establish baseline measurements for holistic KPIs like Customer Lifetime Value and cross-channel conversion rates to benchmark the performance of these initial efforts against the previous siloed approach.
Phase 3: Optimization & Scale (Months 13+)
Building on the successes and learnings from the pilot phase, the strategy is now scaled across the organization. This involves expanding journey mapping and automation to encompass more customer segments and a wider array of behavioral triggers. Additional channels, such as SMS, in-app messaging, and potentially Connected TV, are integrated into the orchestration engine. During this phase, AI and machine learning capabilities should be leveraged more deeply for predictive segmentation, dynamic content personalization, and next-best-action recommendations. The process becomes a continuous cycle of testing, measuring, and refining campaigns based on the holistic performance data and evolving customer behavior.
Future Outlook: The Autonomous Customer Journey
Omnichannel retargeting, as it is understood today, is not an end state. It is a critical evolutionary step toward a future of fully autonomous, AI-driven customer journey management. The convergence of a unified, real-time data foundation (the CDP), powerful predictive AI, and the proliferation of new interfaces (voice, augmented reality, connected devices) will inevitably lead to a paradigm where marketing is less about manually designing and executing campaigns and more about managing an intelligent, self-optimizing system. This system will perpetually tailor individual customer experiences in real time to achieve high-level business objectives like maximizing CLV. The brands that will dominate the future are those that are building the data, technology, and organizational foundation for this reality today.
The transition from channel-centric tactics to a customer-obsessed, omnichannel strategy is a profound and necessary evolution. It demands significant investment in technology, a forward-looking commitment to a first-party data future, and a cultural willingness to restructure teams and incentives around the customer journey. The challenges are substantial, but as the leading brands analyzed in this report demonstrate, the rewards—deeper customer loyalty, sustained revenue growth, and a formidable competitive advantage—are transformative.


